Blog Not Showing on Google?
You’ve gone through all the hard work of creating a new blog post: writing content, creating images, getting internal approval, making revisions, and finally publishing it. You search on Google to see how it ranks, but you can’t find the blog post anywhere!
So, why isn’t your blog showing up on Google?
The most common reasons include: your post hasn’t been indexed yet, it’s blocked by a noindex tag or robots.txt, it lacks internal links, or the content doesn’t meet Google’s quality standards. Fortunately, most of these are fixable; here’s how to diagnose and resolve them.
Quick Navigation:
- Manually Indexing Your Post
- Common Reasons Your Blog Isn’t Showing Up
- Understanding Search Intent
- Optimize for AI and Answer Engines
- Why UX and Readability Impact Your Blog’s Visibility
- How to Get More Visibility
- FAQ
What Happens After You Hit Publish?
Once you publish, Google and AI assistants like Gemini, Perplexity, and Bing AI go through five steps:
- Discover the page
- Crawl it
- Evaluate quality and relevance
- Index it (make it searchable)
- Rank it for specific queries
You might see the message “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” in Search Console. This means Google found the page but hasn’t indexed it yet. That’s normal for new or low-authority content.
But even if crawled, your blog might not be indexed right away. In fact, “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” is a common status in Search Console.
Some reasons:
- Your site is new or has low authority
- The post lacks internal links
- Technical SEO issues (e.g.
noindex, canonical mismatches) - Content doesn’t meet quality thresholds
How can I make sure Google quickly finds my new blog post?
The first thing to know is that Google doesn’t instantly see a blog post the second it goes live. So, if you post a blog today, it might not even be indexed by Google (added to their system) until a few days – or even weeks – later.
Quick Fixes You Can Do Today
One way to speed up Google finding the post is to make sure your sitemap is submitted to Google Search Console and is working correctly.
1. Check Indexing in Search Console
Use the URL Inspection Tool to see if your blog post:
- Hasn’t been indexed
- Is blocked
- Was crawled but not indexed
You can also follow this process to have Google quickly crawl (or re-crawl) your new blog post (or new page) on your website:
A: Go to Google Search Console.
B: Enter the URL for the new post/page in the “Inspect any URL in [site]” field:
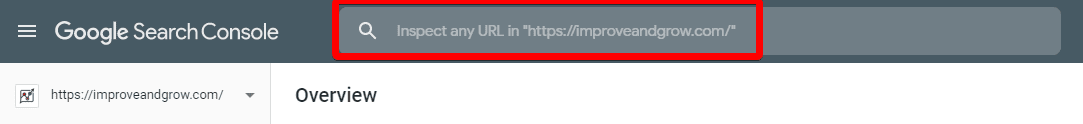
C: On the following page, click “Request Indexing”:
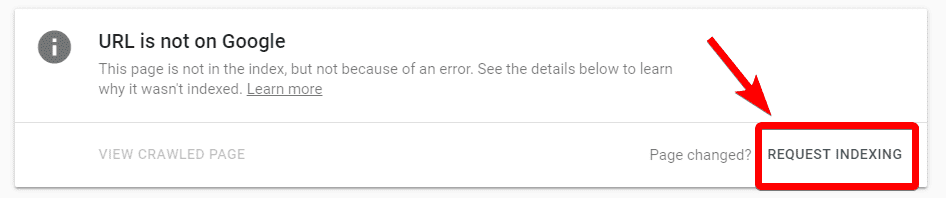
You can also use this Google Search Console feature to identify pages with a ‘noindex’ tag, but failing that you can check for the tag on your page’s source code.
Also check if the page has:
- A
noindexmeta tag - Blocked paths in
robots.txt - Canonical tags pointing elsewhere
Relevant backlinks also help. Share the post on social media, include it in your email newsletter, and request links from relevant websites. Google picks up on third-party signals.
2. Confirm Your Blog Isn’t Blocking Search Engines
Look for these common blockers:
- Noindex meta tags in your page code
- robots.txt settings that disallow crawling
- Canonical tags pointing to other pages
CMS platforms like WordPress sometimes add sitewide noindex settings. Turn these off if they are preventing discovery.
3. Submit and Check Your Sitemap
Your XML sitemap should be up to date and submitted in Search Console. Confirm that your new blog post is included.
Most Common Reasons Your Blog Isn’t Showing Up
Even after requesting indexing, your page may still fail to appear. Here’s what to check:
| Problem | Description | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| “Noindex” meta tag / HTTP header | The page is marked so search engines should not index it. | Check your page HTML (meta robots) or server headers and remove noindex. |
| Robots.txt blocking | The site’s robots.txt may disallow crawling of certain paths. | Visit yourdomain.com/robots.txt and ensure Googlebot is not blocked. |
| Poor or duplicate content | Content is too thin or similar to other pages (including on other sites). | Make your post unique, deeper, more comprehensive. |
| Weak internal linking / orphan content | No or too few internal links point to the post, making it “hard to find.” | From related pages/posts, link into this post. |
| Crawl budget / priority issues | For large sites or low-priority pages, Google’s bots may skip them. | Improve site structure, internal linking, site health, and content value. |
| Canonical / redirect issues | Canonical tags or redirects may tell Google an alternate URL is the “real” one. | Ensure canonical points to the correct version; avoid redirect loops. |
| Site quality / trust / authority problems | If the overall site is weak or lacks authority, Google may deprioritize indexing new pages. | Build E‑E‑A‑T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust), backlinks, content reputation. |
If you’ve manually requested your blog to be indexed, and you’re still not getting ranked where you expect to be, it may be that Google has decided your competitors have better content, or your content isn’t aligned with the queries you think it is. So, prepare to step back, and think deeply about why this might be.
Search engines like Google will always attempt to serve the most helpful, useful content to users based on the queries they search for. After all, it’s what brings users back. Understanding why Google displays content over others involves various factors, let’s dig into these considerations below.
Understanding Searcher Intent
Search engines and AI rank answers, not just pages.
To get ranked (and stay ranked), your blog post needs to align with what users really want when they search your target phrase.
Ask:
- What is the searcher actually trying to solve?
- Do we fully answer that?
- Do we answer related/follow-up questions they might have?
Achieving visibility on Google, for the right keywords, demands a nuanced understanding of searcher intent. Understanding why someone searches for will inform the positioning and crafting of content you want indexed. Ask yourself these key questions
Pro Tip: Check Google’s “People Also Ask” for your main keyword. Use those questions to shape subheadings and FAQs.
What is the Search Intent I’m going for?
This should be the first grounding question you ask yourself when publishing content. This also is the first step in understanding the persona of the audience you are targeting. Once you understand the intention behind the search queries you’re pursuing, you can better anticipate their needs, and begin to answer follow-up questions that person may have.
Conducting thorough keyword research will help you align your content with the right audience and their search intent. Making sure that the intention, or ‘real question’, behind the queries and keywords you’re researching is considered. Some of the best keyword research tools are free (Keyword Planner, Google Trends), and will help you get search volume, similar searches, and more.
Run a few searches for the queries you want to be ranked for take a look at the style, positioning, and formatting of content for top organic results, and compare it with yours. How does it stack up?
⚡Pro tip: check out ‘People Also Ask’ while performing searches you want to rank for – you’ll get insights into the topic you’re trying to gain traction on. You can also use this for thinking up follow-up questions that users might ask.
TL:DR: Navigating search factors requires knowing not just what users search for but why. Strategic keyword research ensures your content resonates with their queries.
Does the Article Address the Searcher’s Question?
Not only must you answer the question or satisfy the intent of the search queries you’re pursuing, but you must do so better than the competition in order to rank well. How effectively does your content answer the query? Is it helpful to the user? There are many nuances to this, but for starters, it’s good practice to make sure that your content provides critical tertiary information about the original query, and possibly answer a few unasked or follow-up questions. Questions that you, as the authoritative publisher would know that the user would need to ask eventually.
TL;DR: Crafting content is about answering the questions users ask. Some questions lead to others, so make sure your content leaves no query or follow-up query unanswered.
Optimize for AI and Answer Engines
Modern search includes AI-powered summaries and direct answers. To increase your visibility:
Structure Content for Clarity
- Use question-based headings
- Include a clearly formatted FAQ section
- Add How-To steps if applicable
Enable AI Inclusion
- Add FAQPage or HowTo schema
- Don’t block bots like GPTBot or PerplexityBot unless necessary
- Cite trustworthy data sources and use confident, accurate language
👉 Want to go deeper on this? Read our full guide: AI SEO Trends for 2026
Looking for help getting your blog content cited by AI tools? We offer dedicated AI optimization services as part of our SEO marketing. Reach out to learn how we can help your content appear in answer engines and conversational search.
Accessibility and UX Still Matter
Even the best content won’t rank (or get cited) if it’s hard to read, slow to load, or buried in poor UX. Prioritize:
- Fast load speeds (90+ on PageSpeed Insights)
- Mobile-first design
- Clear headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs
This one might be deceptively simple. You should optimize content structure for readability use clear headings, and ensure the browsing experience is at least comparable to other websites that answer the same questions. This is where website design and optimization come in.
Imagine you had the perfect answer for a given query, and your competitors had somewhat less perfect answers for the same query. If your website was extremely slow, or the user experience was bad, you’d be risking rank loss on the fact that your website is less useful from a practical accessibility standpoint than competitors.
Think of it this way – if I’m serving pure, ice-cold water, that cannot be delivered in a reasonable time frame or within an appropriate format (let’s say I’m only able to deliver the water in a sponge or bag), it’s safe to assume that a person dying of thirst would prefer a slightly less thirst-slaking solution if it was delivered faster, and in a better format (like a bottle).
⚡Pro Tip: You can use PageSpeed Insights to gauge the speed of the page you’re trying to rank. You can also use it to compare how your page stacks up against competing pages. This is actually a really deep topic that’s covered well in our post about page load times.
TL;DR: Even the most informative content can be overlooked if not presented clearly. Your content placement, style, and organization should not detract from the user’s browsing experience – think page speed, navigation, and stylesheets.
Other Considerations
Are you Truly Leveraging Backlinks?
In Google’s intricate algorithm, backlinks act as endorsements. If your content has existing backlinks, make sure you ask them to align the anchor text to match the intention of your content.
Developing a backlink strategy by contacting industry-related websites, or places your target audience is known to visit is just the beginning. Should should be conducting outreach to improve relations within the online spaces where your content exists, and make suggestions where you think your content would make sense or improve the browsing experience of their users.
For example, I want a backlink to my blog post about how I can save homeowners money by replacing their water heaters. As anchor text for this backlink, I’d like the site owner providing the backlink to include something like ‘reduce utility bill’ or something similar.
⚡Pro Tip: When asking for a backlink, always provide the would-be linker some text to use as anchor text for your content. Anchor text doesn’t have to be your target KW. In all cases, anchor text must make contextual sense in the content wherein it’s placed, so some flexibility is OK.
With the right type of backlinks (and the right amount), you should begin to see that Google is associating your content with a ‘context web’. Pages, posts and domains that contain information around the queries you’re working to rank for.
TL;DR: A backlink’s influence extends beyond its existence; it’s the context that truly matters. Encouraging anchor text that aligns with your content enhances the impact of each link.
Google Isn’t Crawling Your Website
Investigate issues related to the “robots.txt” file, and remove directives blocking URLs you want to show up on Google.
Simply navigate to www.yourdomain.com/robots.txt and check to see if ‘Googlebot’ is being blocked, or if crawling is even encouraged on your site.
What If the Post Is Still Invisible?
Time to audit the content. Ask:
- Is this topic worth ranking for?
- Does it match what users actually want?
- Is it better than competing results?
- Are there enough internal and external signals?
If not, update the content and improve it rather than starting from scratch with a new post.
How can I get more visibility for my blog posts?
You may be wondering “If my blog post isn’t showing in Google, should I keep blogging?”
Just because a blog post doesn’t rank well in Google, doesn’t mean you should stop blogging.
If you’re not getting much traffic to the post, do some keyword research to make sure there’s enough interest in the topic you’re blogging about.
Check Google Search Console to see what terms the post is currently showing up for in search results. Are those relevant? If so, can you add content to the post that includes those queries?
(If none of your blog posts show up in Google, then there are larger internet marketing issues that need to be addressed.)
Blogging for SEO is an Investment
In fact, blogging can be very useful for both SEO and attracting users to the site, but it takes time. It’s a marathon that you started 20+ years ago that you join the moment you start publishing.
I’ve seen this happen with a client in the professional services industry – they consistently created helpful blog posts for years. The blog didn’t start attracting lots of traffic from Google, but the traffic to those posts continued to climb over time. It got to the point where the issue wasn’t as much of “How can we get people to see the article?” but rather “How can we get people deeper on the website to learn more about the business?”.
Want to dive deeper into SEO? Click here >>>
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re managing your blog internally or working with an SEO consultant in Lancaster, PA, it’s crucial to regularly audit your content, ensure proper indexing, and align your publishing strategy with long-term visibility goals.
Trying to figure out why your blog post may not show up in Google may seem frustrating, but there are solutions. Dive into understanding searcher intent, crafting clear content, leveraging backlinks, analyzing user engagement, and resolving common indexing issues. Explore strategies to optimize your blog’s visibility, and make sure it aligns with your overall business strategy.
Looking to enhance your blog’s impact? Check out our guide on the advantages of inbound marketing and effective lead-generation tactics. From content marketing, PPC advertising & management, and expert SEO services to website development, discover practical tips to transform your blog into a powerful tool for attracting and engaging your audience. Explore more ways to generate leads >>
FAQs
How long does it take Google to index a blog post?
It can take anywhere from a few hours to a few weeks, depending on your domain authority, crawl budget, and content quality.
Why does it say “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” in Search Console?
This usually means Google saw the page but didn’t think it was valuable enough to index. Review your content depth and signals.
Will blocking AI bots keep my content private?
Yes, but it also means your content won’t be cited or surfaced by AI assistants. Use a robots.txt or llms.txt to manage.




